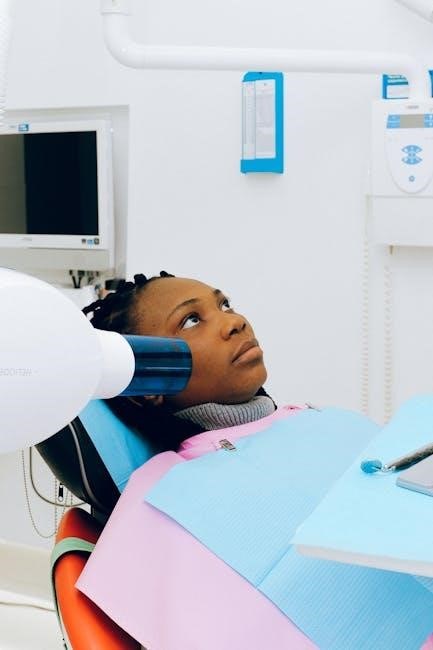
oral mech exam pdf
An oral mechanism exam assesses the structure and function of oral and facial structures, crucial for speech and swallowing. It identifies abnormalities affecting communication and feeding abilities, guiding targeted interventions.
1.1 Importance of Oral Mechanism Exams in Speech Therapy
An oral mechanism exam is vital in speech therapy as it identifies structural and functional abnormalities affecting speech production. By assessing oral motor functions, therapists can uncover underlying issues contributing to articulation or swallowing difficulties. This exam provides crucial insights into the condition of lips, tongue, teeth, and palate, enabling tailored interventions. It also guides adjustments in therapy strategies, ensuring effective treatment plans. Early detection of abnormalities through these exams can significantly improve outcomes, making them a cornerstone in comprehensive speech and language assessment.
1.2 Purpose of Conducting an Oral Mechanism Exam
The primary purpose of an oral mechanism exam is to identify structural or functional abnormalities in the oral and facial structures that may impact speech, swallowing, or feeding. By evaluating the integrity of lips, tongue, teeth, and palate, therapists can assess oral motor skills, symmetry, and range of motion. This exam helps determine the underlying causes of speech or swallowing difficulties, guiding appropriate treatment plans. It also aids in identifying potential barriers to effective communication, ensuring interventions are tailored to the individual’s needs for optimal outcomes.
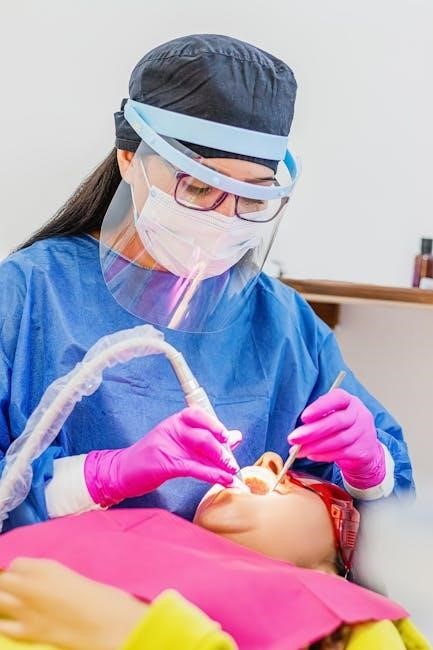
Key Aspects of an Oral Mechanism Exam
An oral mechanism exam evaluates oral structures like lips, tongue, teeth, and palate, assessing range of motion, strength, symmetry, and stimulability to identify motor or structural issues.
2.1 Structures to Examine: Lips, Tongue, Teeth, and Palate
The oral mechanism exam focuses on evaluating the lips, tongue, teeth, and palate. Assessing lip closure, symmetry, and strength is essential for speech production. The tongue’s range of motion, protrusion, and strength are observed to identify motor issues. Teeth alignment and occlusion are examined for their impact on articulation. The palate’s structure and function, including soft palate mobility, are evaluated to ensure proper speech and swallowing mechanisms. These structures are critical for accurate sound formation and overall oral motor function.
2.2 Assessing Range of Motion and Symmetry
Assessing range of motion and symmetry involves evaluating the movement and alignment of oral structures. The tongue’s ability to protrude, lateralize, and elevate is observed. Lip closure and movement symmetry are checked to ensure proper articulation. Jaw mobility, including opening and closing, is assessed for any deviations. Symmetry of the face and oral cavity is evaluated to detect any structural imbalances. These assessments help identify limitations or abnormalities in motor function, which may impact speech and swallowing. Observing these aspects ensures a comprehensive understanding of oral motor capabilities and potential areas for intervention.
2.3 Evaluating Strength and Stimulability
Evaluating strength and stimulability involves testing the oral muscles’ ability to resist pressure and perform specific movements. A tongue depressor may be used to assess tongue strength by applying gentle resistance. Stimulability is measured by prompting the client to perform tasks like sticking out their tongue or moving it side to side. Observing facial muscle strength and symmetry is also crucial. These assessments help identify motor impairments and determine if the client can respond to therapeutic interventions. Findings guide targeted exercises to improve oral motor function and speech clarity.
Oral Mechanism Exam Protocol
The oral mechanism exam protocol involves preparation, step-by-step procedures, and detailed forms to ensure a thorough and efficient assessment. It requires the examiner to know what to look for and how to interpret findings effectively.
3.1 Preparation for the Exam
Preparation for an oral mechanism exam involves gathering necessary tools like tongue depressors, gloves, and examination forms. Ensure good lighting and a comfortable setting for the patient. Review the patient’s history and any previous findings. Familiarize yourself with the exam protocol to ensure efficiency. Provide clear instructions to the patient, explaining each step to promote cooperation. Organize the examination sequence, starting with external observations before moving to internal assessments. Having all materials ready helps streamline the process, ensuring a thorough and effective evaluation of oral structures and functions.
3.2 Step-by-Step Examination Procedures
Begin with external observations of facial symmetry and structure. Assess lip and cheek function by having the patient pucker, smile, and blow. Examine the tongue’s range of motion by asking the patient to protrude, lateralize, and elevate it. Use a tongue depressor to evaluate strength and resistance. Check jaw movement by having the patient open, close, and lateralize their mouth. Observe swallowing and note any irregularities. Evaluate lip closure while drinking from a straw. Ensure each step is performed systematically to gather comprehensive data on oral motor function and structural integrity.
Evaluate jaw motion, dental alignment, lip function, tongue mobility, and palate integrity. Assess symmetry, strength, and stimulability to identify structural or functional deficits impacting speech production.
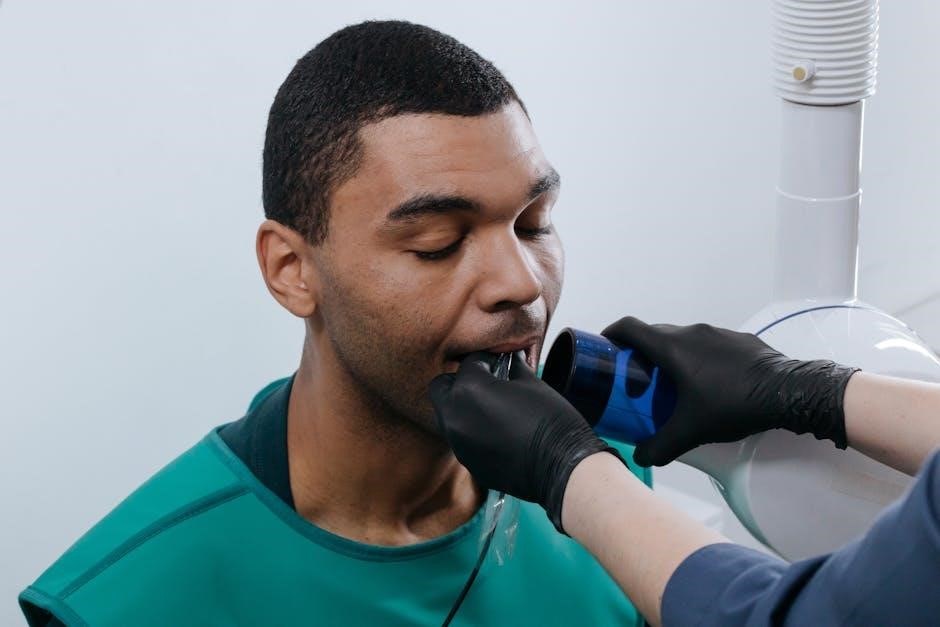
4.1 Evaluation of Jaw and Teeth
Evaluate the jaw’s range of motion, symmetry, and alignment. Assess teeth for occlusion, wear, or misalignment. Note any pain or dysfunction during movement. Ensure proper jaw function for speech and swallowing, addressing issues like limited motion or asymmetry that may impact articulation or chewing efficiency, and check for signs of temporomandibular joint issues. Proper dental alignment is crucial for clear speech production, and any abnormalities may indicate the need for orthodontic or prosthetic interventions to improve oral motor function and overall communication abilities.
4.2 Observation of Lip and Cheek Function
Assess lip and cheek function by evaluating symmetry, strength, and movement. Observe lip closure during speech and at rest. Check for any signs of weakness or asymmetry. Test stimulability by asking the individual to pucker or blow. Note cheek tension and retraction, especially during activities like drinking from a straw. Evaluate resistance by gently pressing a tongue depressor against the lips. Abnormalities in lip or cheek function may indicate motor deficits, affecting speech articulation and swallowing. Proper function is essential for clear speech production and feeding abilities, making this assessment critical for targeted therapy planning and intervention strategies.
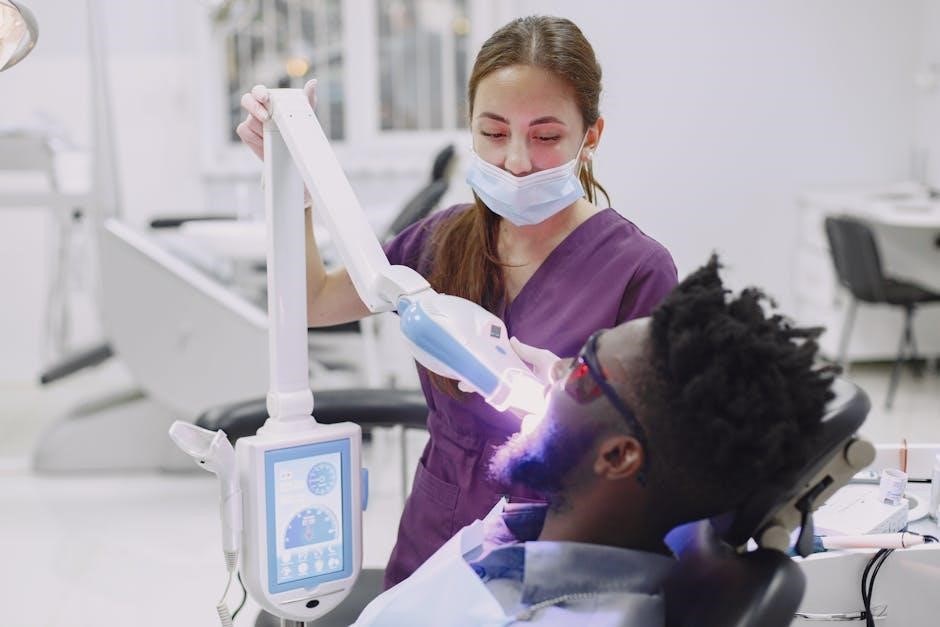
Assessment of Specific Oral Structures
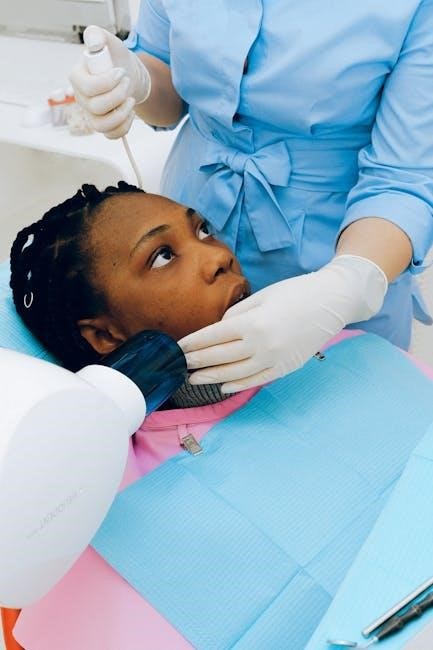
4;3 Detailed Tongue Assessment
A detailed tongue assessment evaluates symmetry, range of motion, strength, and stimulability. Begin by observing the tongue at rest for size, shape, and symmetry. Ask the individual to protrude, elevate, and lateralize the tongue, noting any limitations. Test strength by pressing a tongue depressor against the protruded tongue, assessing resistance. Evaluate speech sounds requiring precise tongue movements; Check for fasciculations or atrophy. Abnormal findings may indicate neurological or structural issues, impacting speech clarity and swallowing. This assessment guides targeted therapy to improve oral motor skills and overall communication effectiveness, ensuring comprehensive care.
Findings and Their Implications
Findings from an oral mechanism exam reveal structural or functional abnormalities, guiding differential diagnosis of speech disorders. These insights inform targeted interventions, improving communication and swallowing outcomes effectively.
5.1 Identifying Structural or Functional Abnormalities
An oral mechanism exam identifies structural or functional abnormalities in oral and facial structures. The examiner visually inspects for asymmetries, signs of weakness, or atypical movements. Key observations include lip, tongue, and jaw function, as well as palate structure. Any deviations from normal anatomy or movement patterns are noted. This assessment helps detect issues like tongue-tie, cleft palate, or neuromuscular dysfunction. Functional abnormalities, such as limited range of motion or poor coordination, are also evaluated. These findings are critical for diagnosing underlying causes of speech or swallowing difficulties, ensuring appropriate interventions are developed.
5.2 Differential Diagnosis of Speech Sound Disorders
The oral mechanism exam plays a crucial role in differential diagnosis by providing insights into structural and functional factors affecting speech. Observations of lip movement, tongue symmetry, jaw alignment, and palate function help identify underlying causes of speech sound disorders. For instance, limited tongue range of motion may indicate a neurological issue, while misaligned teeth could suggest an orthodontic cause. These findings aid in distinguishing between articulation, phonological, or motor-based disorders. Accurate diagnosis enables targeted interventions, ensuring therapies address the root cause of speech difficulties, leading to more effective treatment outcomes for individuals with communication challenges.
Referrals and Collaborative Care
Referrals to specialists like orthodontists or ENTs are essential when structural issues are identified. Collaborative care ensures comprehensive treatment, involving speech therapists, occupational therapists, and medical professionals.
6.1 When to Refer to Specialists
Referrals to specialists are necessary when structural or functional abnormalities are detected during an oral mechanism exam. Conditions such as jaw misalignment, cleft palate, or significant weakness in oral muscles may require consultation with orthodontists, ENT specialists, or neurologists. If speech or swallowing difficulties persist despite therapy, further evaluation by a multidisciplinary team is recommended. Timely referrals ensure comprehensive care and address underlying issues that may impact treatment outcomes. Collaborative efforts between speech-language pathologists and other healthcare professionals are critical for effective management and intervention.
6.2 Role of Interdisciplinary Teams in Diagnosis
Interdisciplinary teams play a vital role in diagnosis by combining expertise from speech-language pathologists, orthodontists, ENT specialists, and occupational therapists. Collaborative efforts ensure a holistic understanding of oral mechanism findings, linking structural issues to functional impairments. Shared insights facilitate accurate diagnoses, particularly for complex cases involving multiple systemic factors. Teamwork enhances the development of tailored intervention plans, addressing both speech and related physical challenges. This integrated approach maximizes therapeutic outcomes, ensuring comprehensive care for individuals with oral motor or swallowing difficulties, and underscores the importance of a coordinated diagnostic process.
Documentation and Reporting
Accurate documentation of oral mechanism exam findings is essential for tracking progress and planning interventions. Detailed reports include observations, measurements, and clinical impressions, ensuring clear communication among professionals.
7.1 Completing the Oral-Facial Examination Form
The oral-facial examination form is a structured tool for documenting findings from the oral mechanism exam. It includes sections for assessing facial symmetry, lip function, tongue movement, and dental alignment. Clinicians check and circle observations, noting abnormalities or deviations from typical anatomy and function. Descriptive comments are added to provide context for specific findings. The form is organized sequentially, starting with external structures and progressing to internal oral mechanisms. This ensures a thorough and systematic recording of data, which is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. Clear documentation supports effective communication among healthcare professionals and informs future interventions.
7.2 Interpreting and Sharing Results
Interpreting oral mechanism exam results involves analyzing data from the examination form to identify structural or functional abnormalities. Clinicians review findings, such as limited tongue movement or asymmetrical facial features, to determine their impact on speech and swallowing. Results are shared with interdisciplinary teams, including speech therapists, dentists, and medical specialists, to facilitate collaborative care. Clear communication of findings ensures targeted interventions and supports differential diagnosis. Detailed reports are often provided to clients or guardians, outlining recommendations for therapy or further evaluation. This step is critical for developing personalized treatment plans and monitoring progress over time.
An oral mechanism exam is integral to comprehensive care, providing insights into structural and functional abnormalities. It guides targeted interventions, ensuring effective speech and swallowing therapy outcomes.
8.1 The Role of Oral Mechanism Exams in Comprehensive Care
Oral mechanism exams play a vital role in comprehensive care by identifying structural and functional abnormalities. They guide targeted interventions, ensuring effective speech and swallowing therapy outcomes. These exams provide clinicians with essential insights, enabling personalized treatment plans. By assessing oral motor function, they help address articulation and feeding challenges, promoting overall communication and nutritional well-being. Regular exams ensure timely adjustments to therapy, optimizing patient progress and long-term success. Thus, they are indispensable in holistic patient care, bridging the gap between assessment and effective intervention.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.